Answer:
The correct answer is option d.
Step-by-step explanation:
A monopolistic firm is producing 12000 units at a price of $10 per units.
The average variable cost per unit is $6/unit.
The fixed costs are $15,000.
The average fixed costs will be
=
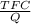
=
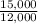
=1.25
The average total cost is
=average fixed cost+average variable cost
=$(6+1.25) per unit
=$7.25 per unit
Here, the price per unit is greater than average total cost per unit. This means that the firm is having supernormal profits. This will attract other firms to join the market.
In the long run, when new firms enter the market, the market supply will increase leading to a fall in price.