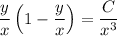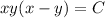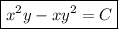The ODE is exact, since
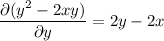
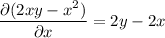
so there is solution
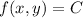 such that
such that
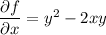
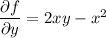
Integrating both sides of the first PDE wrt
 gives
gives
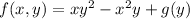
Differentiating both sides wrt
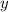 gives
gives
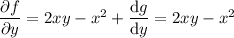
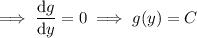
Then the solution to the ODE is
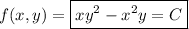
# # #
Alternatively, we can see that the ODE is homogeneous, since replacing
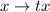 and
and
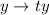 reduces to the same ODE:
reduces to the same ODE:
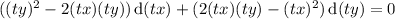
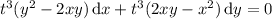
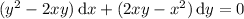
This tells us we can solve by substituting
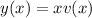 , so that
, so that
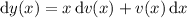 , and the ODE becomes
, and the ODE becomes
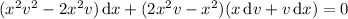
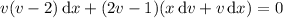
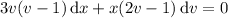
which is separable as
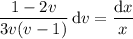
Integrating both sides gives
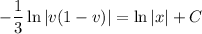
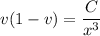
and solving in terms of
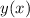 ,
,