Answer:
a.1.71 eV
b.0.939 nm
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given that
Wavelength of light =310 nm=
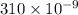 m
m
Work function=2.3 eV
Mass of electron=
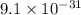 Kg
Kg
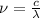
a.We have to find the maximum kinetic energy of ejected electron
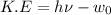
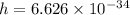
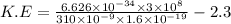
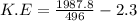
K.E=1.71 eV
Hence, the maximum kinetic energy of ejected electron=1.71 eV
b.Kinetic energy =
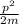
p=
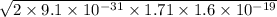
p=
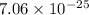 m-s
m-s
We know that de brogile wavelength
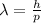
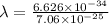
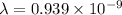
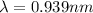
Hence, the de-brogile wavelength of ejected electron=0.939 nm.