Answer:
The volume of the sample if the temperature is increased to 206°C when the pressure is kept constant is 3,463.07 cm³.
Step-by-step explanation:
Charles's Law consists in the relationship between the volume and temperature of a certain amount of ideal gas, where constant pressure is maintained. The relationship is produced by means of a constant of proportionality. Then, at a constant pressure, as the temperature increases, the volume of the gas increases and as the temperature decreases, the volume of the gas decreases.
In summary, Charles's law is a law that says that when the amount of gas and pressure remain constant, the ratio between volume and temperature will always have the same value:
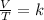
It is now possible to assume that you have a certain volume of V1 gas that is at a temperature V1 at the beginning of the experiment. If you vary the volume of gas to a new V2 value, then the temperature will change to T2, and it will be met:
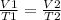
In this case:
- V1=2135 cm³
- T1=127 °C
- V2=?
- T2=206 °C
Then:
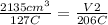
Solving you get:
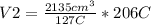
V2=3,463.07 cm³
The volume of the sample if the temperature is increased to 206°C when the pressure is kept constant is 3,463.07 cm³.