Answer:
4.75A, 479W
Step-by-step explanation:
The power P, taken by an appliance is related to the current I, drawn by the appliance and the voltage V, at which it is operating as follows;
P = I x V -------------------(i)
From the question, the appliance is the electric heater and;
P = 570W
V = 120V
Substitute these values into equation (i) as follows;
570 = I x 120
i =
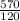
I = 4.75
Therefore, the current that it draws is 4.75A
(b) First, lets find the resistance, R, in the heater as follows;
P =
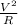 -----------------------(ii)
-----------------------(ii)
Where;
P = Power
V = Voltage
Substitute V=120V and P=570W into equation (ii) as follows;
570 =
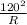
Cross multiply and solve for R;
570R = 120²
570R = 14400
R =
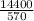
R = 25.26Ω
The resistance of the heater is 25.26Ω
Now, if the voltage drops to 110V and resistance is assumed to be constant, then using equation (ii);
P =
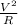
...we can calculate the power the heater takes by substituting V=110V and R = 25.26Ω as follows;
P =
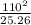
P = 479
Therefore, the power the heater takes is 479W