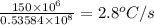Answer:
The temperature of the core raises by
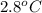 every second.
every second.
Step-by-step explanation:
Since the average specific heat of the reactor core is 0.3349 kJ/kgC
It means that we require 0.3349 kJ of heat to raise the temperature of 1 kg of core material by 1 degree Celsius
Thus reactor core whose mass is
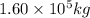 will require
will require
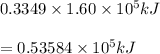
energy to raise it's temperature by 1 degree Celsius in 1 second
Hence by the concept of proportionately we can infer 150 MW of power will increase the temperature by