Answer: Radio waves have a wavelength that is comparable in size with buildings, that is why it bends (diffracts) around them. On the other hand, X-rays wavelength is so small compared with the size of a building and even a wall, that it is impossible for this invisible light to bend around a wall.
This "bending" of the waves described here is formally known as Diffraction.
In this sense, diffraction happens when a wave (mechanical or electromagnetic wave) meets an obstacle or slit. When this occurs, the wave bends around the edges of the obstacle or passes through the opening of the slit that acts as an obstacle.
In this case we are talking about two types of electromagnetic waves (light):
-Radio waves with a wavelength between
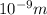 and
and
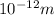
-X rays with a wavelength between
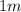 and
and
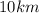
Now, it is important to note that the principal condition for the occurrence of diffraction is that the obstacle must be comparable in size (similar size) to the size of the wavelength.
This means:
Radio waves have a wavelength that is comparable in size with buildings, that is why it bends (diffracts) around them. On the other hand, X-rays wavelength is so small compared with the size of a building and even a wall, that it is impossible for this invisible light to bend around a wall.
Therefore, if the technician stands behind a wall during the use of the X-ray machine, she will be safe.