Answer:
(a) P2 = 8 atm, T2 = 300 K, W = 3458.32 J
(b) P2 = 32 atm, T2 = 1200 K, W = 9696 J
Step-by-step explanation:
P1 = 32 atm
V1 = 1 L
V2 = 4 L
T1 = 300 K
(a) When the process is isothermal
The temperature remains constant, so the final temperature, T2 = 300 k
Use
P1 x V1 = P2 x V2
32 x 1 = P2 x 4
P2 = 8 atm
So, the final pressure is 8 atm and the final temperature is 300 K
Work done in isothermal expansion is given by
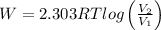
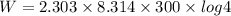
W = 3458.32 J
(b) When the process is isobaric
the pressure remains constant, so the final pressure, P2 = 32 atm
Use
V1 / T1 = V2/ T2
1 / 300 = 4 / T2
T2 = 1200 K
Work done in isobaric process
W = P (V2 - V1) = 32 x (4 - 1) = 96 atm L
W = 96 x 1.01 x 10^5 x 10^-3 = 9696 J