a)
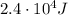
For a gas transformation occuring at a constant pressure, the work done by the gas is given by
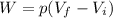
where
p is the gas pressure
V_f is the final volume of the gas
V_i is the initial volume
For the gas in the problem,
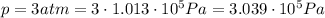 is the pressure
is the pressure
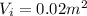 is the initial volume
is the initial volume
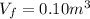 is the final volume
is the final volume
Substituting,
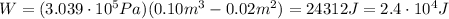
b)
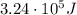
The heat absorbed by the gas can be found by using the 1st law of thermodynamics:
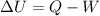
where
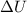 is the change in internal energy of the gas
is the change in internal energy of the gas
Q is the heat absorbed
W is the work done
Here we have
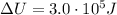
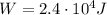
So we can solve the equation to find Q:
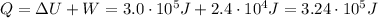
And this process is an isobaric process (=at constant pressure).