Answer:
Lattice constant, d = 1.3 nm
Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Wavelength,
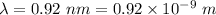
You observe the first diffraction peak at an angle of 20.6°,
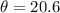
Using Bragg's diffraction law as :
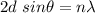
Here, n = 1
d = lattice constant
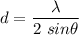
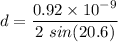
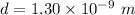
or
d = 1.3 nm
So, the lattice constant of the crystal is 1.3 nm. Hence, this is the required solution.