Answer : The partial pressure of
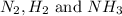 at equilibrium are, 1.133, 2.009, 0.574 bar respectively. The total pressure at equilibrium is, 3.716 bar
at equilibrium are, 1.133, 2.009, 0.574 bar respectively. The total pressure at equilibrium is, 3.716 bar
Solution : Given,
Initial pressure of
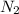 = 1.42 bar
= 1.42 bar
Initial pressure of
 = 2.87 bar
= 2.87 bar
 = 0.036
= 0.036
The given equilibrium reaction is,
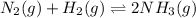
Initially 1.42 2.87 0
At equilibrium (1.42-x) (2.87-3x) 2x
The expression of
 will be,
will be,
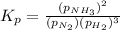
Now put all the values of partial pressure, we get
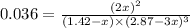
By solving the term x, we get
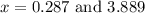
From the values of 'x' we conclude that, x = 3.889 can not more than initial partial pressures. So, the value of 'x' which is equal to 3.889 is not consider.
Thus, the partial pressure of
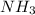 at equilibrium = 2x = 2 × 0.287 = 0.574 bar
at equilibrium = 2x = 2 × 0.287 = 0.574 bar
The partial pressure of
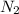 at equilibrium = (1.42-x) = (1.42-0.287) = 1.133 bar
at equilibrium = (1.42-x) = (1.42-0.287) = 1.133 bar
The partial pressure of
 at equilibrium = (2.87-3x) = [2.87-3(0.287)] = 2.009 bar
at equilibrium = (2.87-3x) = [2.87-3(0.287)] = 2.009 bar
The total pressure at equilibrium = Partial pressure of
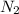 + Partial pressure of
+ Partial pressure of
 + Partial pressure of
+ Partial pressure of
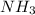
The total pressure at equilibrium = 1.133 + 2.009 + 0.574 = 3.716 bar