I'll leave the computation via R to you. The
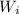 are distributed uniformly on the intervals
are distributed uniformly on the intervals
![[0,10i]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/haeg5rzkfl1jssxgzd9n8rswwzewzd6q6c.png) , so that
, so that
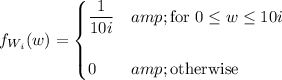
each with mean/expectation
![E[W_i]=\displaystyle\int_(-\infty)^\infty wf_(W_i)(w)\,\mathrm dw=\int_0^(10i)\frac w{10i}\,\mathrm dw=5i](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/2gxi5wxgtwj52x4vanxq1cozq4brf0svrl.png)
and variance
![\mathrm{Var}[W_i]=E[(W_i-E[W_i])^2]=E[{W_i}^2]-E[W_i]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/qrtyo1tqznppjtpzgzdmnv9r0ws9a7shgw.png)
We have
![E[{W_i}^2]=\displaystyle\int_(-\infty)^\infty w^2f_(W_i)(w)\,\mathrm dw=\int_0^(10i)(w^2)/(10i)\,\mathrm dw=\frac{100i^2}3](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/g2313d1cjkuow864tld83nkjsu0i9n2n1x.png)
so that
![\mathrm{Var}[W_i]=\frac{25i^2}3](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/lsubdy6gag75f3gqowjb801ix70otp9bwh.png)
Now,
![E[W_1+W_2+W_3]=E[W_1]+E[W_2]+E[W_3]=5+10+15=30](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/zmrifppc2l6r7choju186x9s20joonsvwx.png)
and
![\mathrm{Var}[W_1+W_2+W_3]=E\left[\big((W_1+W_2+W_3)-E[W_1+W_2+W_3]\big)^2\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/oliylqtmh3nmyycvpua5s2q6d6l97gffk8.png)
![\mathrm{Var}[W_1+W_2+W_3]=E[(W_1+W_2+W_3)^2]-E[W_1+W_2+W_3]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/s460z9zrbiasxpw8phsyj6un295fwxqt1h.png)
We have
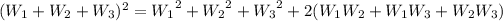
![E[(W_1+W_2+W_3)^2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/arwdm5b6bkr9xr9jaarpm7mvyyn59motd6.png)
![=E[{W_1}^2]+E[{W_2}^2]+E[{W_3}^2]+2(E[W_1]E[W_2]+E[W_1]E[W_3]+E[W_2]E[W_3])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/fnyy7dg166o3b7ph94oi2avyh2wm32q3e5.png)
because
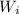 and
and
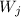 are independent when
are independent when
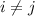 , and so
, and so
![E[(W_1+W_2+W_3)^2]=\frac{100}3+\frac{400}3+300+2(50+75+150)=\frac{3050}3](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/vdi5apg8mim9bvevhuzninewfgmnniuyf8.png)
giving a variance of
![\mathrm{Var}[W_1+W_2+W_3]=\frac{3050}3-30^2=\frac{350}3](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/tcmrvl817uynf48ev05e4jjf1h65ed714t.png)
and so the standard deviation is
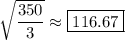
# # #
A faster way, assuming you know the variance of a linear combination of independent random variables, is to compute
![\mathrm{Var}[W_1+W_2+W_3]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/ncsae94xxdi5ymk1wmbg3x8vm291ge6sq2.png)
![=\mathrm{Var}[W_1]+\mathrm{Var}[W_2]+\mathrm{Var}[W_3]+2(\mathrm{Cov}[W_1,W_2]+\mathrm{Cov}[W_1,W_3]+\mathrm{Cov}[W_2,W_3])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/289opnz7fp4ufr7y527jffv30m0sqffxuw.png)
and since the
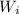 are independent, each covariance is 0. Then
are independent, each covariance is 0. Then
![\mathrm{Var}[W_1+W_2+W_3]=\mathrm{Var}[W_1]+\mathrm{Var}[W_2]+\mathrm{Var}[W_3]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/qdlquvydteqgwaf8q4jcddxysfaspexf5s.png)
![\mathrm{Var}[W_1+W_2+W_3]=\frac{25}3+\frac{100}3+75=\frac{350}3](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/to1l758fb1d9m9crovhm4ybm0o6wf9wzns.png)
and take the square root to get the standard deviation.