Step-by-step explanation:
The linear analog of angle is angle itself.
The linear analog of angular velocity is linear velocity.
ω is angular velocity, therefore linear velocity is given by v
∴ for linear velocity,
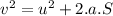
for angular velocity,
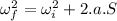
The linear analog of angular acceleration is acceleration.
α is angular acceleration whereas as a is linear acceleration.
∴ for linear acceleration, v = u + a.t
for angular acceleration,
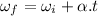
The linear analog of moment of inertia is mass.
I is moment of inertia and m is mass,
∴ for linear analog, F = m.a
for angular analog, τ - I.α