Step-by-step explanation:
According to Langmuir isotherm,
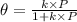
where,
 = fraction coverage by gas molecules
= fraction coverage by gas molecules
k = rate constant
P = partial pressure of gas
Also,
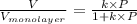
or
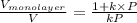
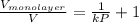
k =
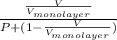
Now, equation
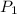 and
and
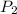 for
for
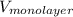 as follows.
as follows.
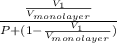 =
=
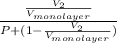
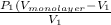 =
=
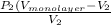
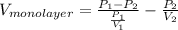 .......... (1)
.......... (1)
As it is given that
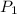 is 56.4 kPa,
is 56.4 kPa,
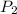 is 108 kPa,
is 108 kPa,
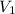 is
is
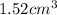 and
and
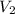 is
is
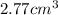 .
.
Therefore, putting these values into equation (1) as follows.
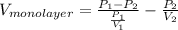
=
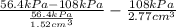
= 27.44
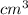
Thus, we can conclude that volume of monolayer is 27.44
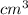 .
.