Answer:
[COCl₂] = 0.373 mol·L⁻¹
[CO] = [Cl₂] = 0.069 mol·L⁻¹
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced equation is
CO + Cl₂ ⇌ COCl₂
Data:
Kc = 77.5
n(CO₂) = 0.442 mol
n(Cl₂) = 0.442 mol
V = 1.00 L
1. Calculate the initial concentration of CO and Cl₂
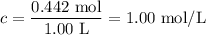
Step 2. Set up an ICE table.
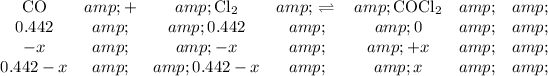
Step 3. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations
![K_{\text{c}} = \frac{\text{[COCl$_(2)$]}}{\text{[CO][Cl$_2$]}} = (x)/((0.442 - x)^(2)) = 77.5\\\begin{array}{rcl}\\(x)/((0.442 - x)^(2)) & = & 77.5\\\\x & = & 77.5(0.442 - x)^(2)\\x & = & 77.5(0.1954 - 0.884x + x^(2)\\x & = & 15.14 - 68.51x + 77.5x^(2)\\77.5x^(2) - 69.51x + 15.14 & = & 0\\x & = & \mathbf{0.373}\\\end{array}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ko4cvwr3jofvm985uhih4t48y09rmcj1nt.png)
[COCl₂] = x mol·L⁻¹ = 0.373 mol·L⁻¹
[CO] = [Cl₂] = (0.442 - 0.373) mol·L⁻¹ = 0.069 mol·L⁻¹