Answer:
For a: The number of moles of oxygen gas is 0.74375 moles.
For b: The energy transferred to oxygen as heat is
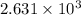
For c: The fraction of heat used to raise the internal energy of oxygen is 0.714.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
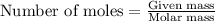
Given mass of oxygen gas = 23.8 g
Molar mass of oxygen gas = 32 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
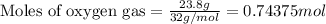
Hence, the number of moles of oxygen gas is 0.74375 moles.
Oxygen is a diatomic gas.
To calculate the amount of heat transferred, we use the equation:
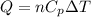
where,
Q = heat absorbed or released
n = number of moles of oxygen gas = 0.74375 moles
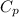 = specific heat capacity at constant pressure =
= specific heat capacity at constant pressure =
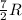 (For diatomic gas)
(For diatomic gas)
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K
 = change in temperature =
= change in temperature =
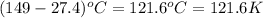
Putting values in above equation, we get:
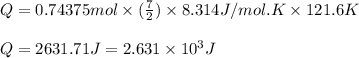
Hence, the energy transferred to oxygen as heat is
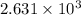
To calculate the fraction of heat, we use the equation:
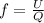
where,
U = internal energy =
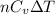
Calculating the value of U:
n = number of moles of oxygen gas = 0.74375 moles
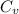 = specific heat capacity at constant pressure =
= specific heat capacity at constant pressure =
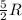 (For diatomic gas)
(For diatomic gas)
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K
 = change in temperature =
= change in temperature =
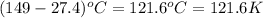
Putting values in above equation, we get:
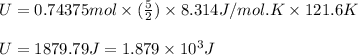
Taking the ratio of 'U' and 'Q', we get:
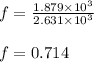
Hence, the fraction of heat used to raise the internal energy of oxygen is 0.714.