Answer:
Power consume by compressor=113,726.87 KW
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
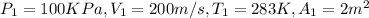
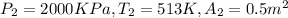
Actually compressor is an open system, so here we will use first law of thermodynamics for open system .
We know that first law of thermodynamics for steady flow
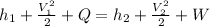
We know that
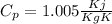 and we take the air as ideal gas.
and we take the air as ideal gas.
System is in steady state then mass flow rate in =mass flow rate out
Mass flow rate=
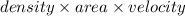
So mass flow rate =
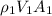 ,
,
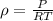
=1.23×200×2 Kg/s
=541.17 Kg/s
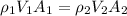
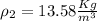 ,
,
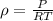
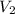 =80.07 m/s
=80.07 m/s
Enthalpy of ideal gas h=
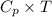
So
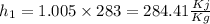
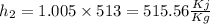
Now by putting the values
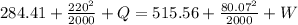
Here Q=0 because heat transfer is zero here.
W= -210.15 KJ/kg
So power consume by compressor=541.17×210.15
=113,726.87 KW