Answer:
The heat of reaction for the combustion of a mole of Ti in this calorimeter is
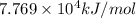 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
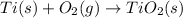
Moles of titanium =
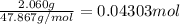
Heat absorbed by the bomb caloriometer on combustion of 0.04303 mol of titanium be Q
The heat capacity of the bomb caloriometer =c = 9.84 kJ/K
Change in temperature of the bomb caloriometer :
=ΔT=91.60 °C-25.00 °C=66.6 °C = 339.75 K
Q = c × ΔT
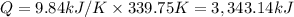
3,343.14 kJ of heat energy was released when 0.04303 moles of titanium undergone combustion.
So for 1 mol of titanium:
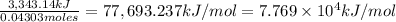
The heat of reaction for the combustion of a mole of Ti in this calorimeter is
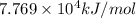 .
.