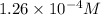Answer: The hydroxide ion concentration is
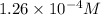
Step-by-step explanation:
pOH is defined as the negative logarithm of hydroxide ion concentration in the solution.
To calculate the pOH of the reaction, we use the equation:
![pOH=-\log[OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/n477c3o3xy8p6ug3ipfjqh9fd53hdrrjyq.png)
where,
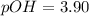
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![3.90=-\log[OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/tn2vz7csv9onre37wao5b6xiixlh5c2rpd.png)
![[OH^-]=1.26* 10^(-4)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/fk2oymgn82tn9lyf663nt2gzhjspi2iuni.png)
Hence, the hydroxide ion concentration is