Answer:
True options:
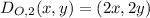
Side Q'S' lies on a line with a slope of -1.
The distance from Q' to the origin is twice the distance from Q to the origin.
Explanation:
Triangle QRS is dilated according to the rule
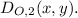 This dilation has the rule
This dilation has the rule
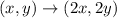
So,
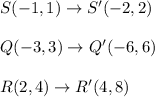
True options:
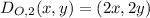
Side Q'S' lies on a line with a slope of -1.
The distance from Q' to the origin is twice the distance from Q to the origin.
False options:
QR is longer than Q'R', because QR is twice shorter than Q'R'.
The vertices of the image are closer to the origin than those of the pre-image, because the vertices of the per-image are closer to the origin than those of the image (see attached diagram).