(a) The acceleration doubles
According to Newton's second law, the acceleration of the object can be written as
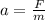
where
F is the force exerted on the object
m is the mass of the object
Let's now analyze what happens when the force is doubled:
F' = 2F
In this case, the new acceleration is
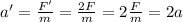
So, the acceleration also doubles.
(b) The acceleration will halve
The initial acceleration is:
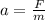
This time, the object's mass is doubled, so
m' = 2m
Therefore, the new acceleration will be:
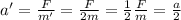
So, the acceleration will halve, since it is inversely proportional to the mass.
(c) The acceleration does not change
The initial acceleration is:
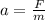
In this case, both the force and the mass are doubled, so:
F' = 2F
m' = 2m
So, the new acceleration is
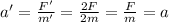
so, the acceleration has not changed.
(d) The acceleration will quadruple
The initial acceleration is:
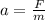
In this case, the force is doubled and the mass is halved, so:
F' = 2F
m' = m/2
Therefore, the new acceleration is
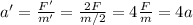
so, the acceleration is quadrupled.