Answer:
The correct answer is:'by emitting a beta particle'.
Step-by-step explanation:
An atom with too many neutron relativity in comparison to number of proton will under radioactive decay by the means of beta-decay.
Beta-decay is a radioactive decay process in which a neutron gets converted to into proton and electron as a beta-particle with (-1)charge.
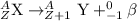
So , by emitting a beta-particle an atom with more number of neutrons than protons will under radioactive decay.