Answer: The correct answer is Option C.
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given two reactions:
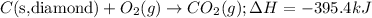 ....(1)
....(1)
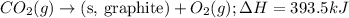 ....(2)
....(2)
According to Hess’s law of constant heat summation, the heat absorbed or released in a given chemical equation is the same whether the process occurs in one step or several steps.
For the reaction of conversion of diamond to graphite, the equation follows:
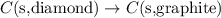
The enthalpy of the above reaction is given as:
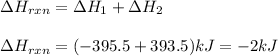
As, the enthalpy change for the reaction is coming out to be negative. Thus, it is getting released during the process.
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.