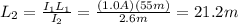Answer:
21.2 m
Step-by-step explanation:
The current in the wire is given by Ohm's law:
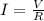
where V is the voltage of the battery and R is the resistance of the wire.
The resistance of the wire is directly proportional to the length of the wire, so we can write:
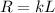
where k is a constant and L is the length of the wire. Substituting into the first equation,
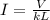
We can rewrite this equation also as
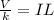
where the term on the left is a constant (because the voltage of the battery does not change). So, we can write:
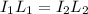
where:
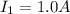 is the current in the first situation
is the current in the first situation
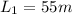 is the length of the wire in the first situation
is the length of the wire in the first situation
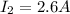 is the current in the second situation
is the current in the second situation
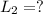 is the length of the wire in the second situation
is the length of the wire in the second situation
Re-arranging the formula, we can find the value of L2: