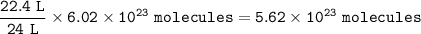Both containers have the same number of molecules= 5.62 x 10²³
Further explanation
Given
22.4 L of hydrogen gas
22.4 L of oxygen gas
25°C and 1 atm.
Required
true statement
Solution
Conditions at T 25 ° C and P 1 atm are stated by RTP (Room Temperature and Pressure). Vm in this condition = 24 liters / mol
and from Avogadro's Law :
At the same temperature and pressure, the ratio of gas volume will be equal to the ratio of gas moles
So two gas have the same molecules
1 mol = 6.02 x 10²³ molecules
24 L = 1 mol, so for 22.4 L :