Answer: the volume of O2 gas is produced from 3.20 liters of CO2 at STP is 1.60 L
To solve this problem you must first balance the chemical equation of it,
2Na2O2 + 2CO2 → 2Na2CO3 + O2
After balancing the reaction we can see that for every 2 moles of CO2, 1 mol of O2 is produced, by virtue of the estequimetric coefficients of these chemical species in the equation.
According to IUPAC, STP (Standard conditions for Temperature and Pressure) is defined as a temperature of 273.15 K and an absolute pressure of exactly 1 bar which is equal to 0.986923 atm
To know the volume of O2 that are produced from 3.20 L of CO2 to STP, we must first calculate the amount of O2 moles that are produced from the moles of CO2 present.
According to the law of ideal gases:
PV = nRT
Where P, V, n and T are the pressure, volume, moles and temperature of the gas in question while R is the gas constant (0.082057 atm L / mol K)
Then, the moles of CO2 present from 3.20 L of this gas to STP will be,
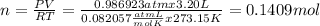
Then, the moles produced of O2 from 0.1409 moles of CO2 are,
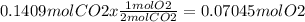
And the volume of O2 will be, according to the equation of ideal gases,
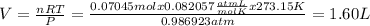
It can be observed that,
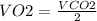
So, the volume of O2 gas is produced from 3.20 liters of CO2 at STP is 1.60 L