Explanation :
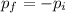
Momentum of a body is defined as the product of its mass and velocity.
i.e.
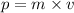
So, when an object is moving, it has momentum.
If
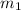 and
and
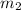 are the masses of objects A and B and
are the masses of objects A and B and
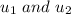 are their initial velocities. so, their initial momentum will be:
are their initial velocities. so, their initial momentum will be:
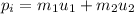
If after collision it bounces back with same velocities, then final momentum becomes:
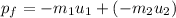
-ve sign shows that the motion is in opposite direction.
so,
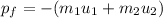
or
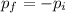
Hence, its final momentum is in opposite direction of initial momentum.