For this case we have a system of two equations with two unknowns.
To solve, we equate both equations:
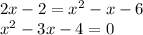
We have a quadratic equation of the form:
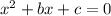
Where:
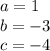
Its roots are given by:
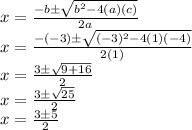
We have two roots:
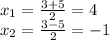
Thus, we look for the values of y, by substituting any of the equations:
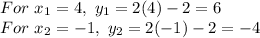
Answer:
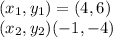
Option B