Answer:
![\left[ (4)/(3),4 \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/2pymrrtbywawxi5247k0z5jlk093r38tkz.png)
Explanation:
Inequality 1
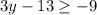
Add 13 to both sides:
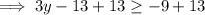
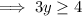
Divide both sides by 3:
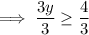
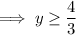
Therefore, y is equal to or bigger than 4/3.
Inequality 2
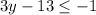
Add 13 to both sides:
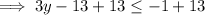
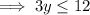
Divide both sides by 3:
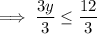
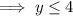
Therefore, y is equal to or smaller than 4.
Therefore, the solution to the inequalities in interval notation is:
![\left[ (4)/(3),4 \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/2pymrrtbywawxi5247k0z5jlk093r38tkz.png)