Answer:
impulse acting on it
Step-by-step explanation:
The impulse is defined as the product between the force applied to an object (F) and the time interval during which the force is applied (
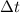 ):
):
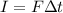
We can prove that this is equal to the change in momentum of the object. In fact, change in momentum is given by:
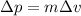
where m is the mass and
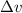 is the change in velocity. Multiplying and dividing by
is the change in velocity. Multiplying and dividing by
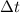 , we get
, we get
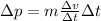
and since
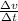 is equal to the acceleration, a, we have
is equal to the acceleration, a, we have
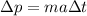
And since the product (ma) is equal to the force, we have
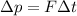
which corresponds to the impulse.