Answer:
Approximately
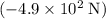 (rounded to two significant figures.)
(rounded to two significant figures.)
Step-by-step explanation:
The impulse
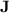 on an object is equal to the change in the momentum
on an object is equal to the change in the momentum
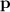 of this object. Dividing impulse by duration
of this object. Dividing impulse by duration
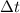 of the contact would give the average external force that was exerted on this object.
of the contact would give the average external force that was exerted on this object.
If an object of mass
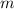 is moving at a velocity of
is moving at a velocity of
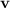 , the momentum of that object would be
, the momentum of that object would be
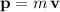 .
.
Let
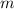 denote the speed of this ball. Let
denote the speed of this ball. Let
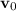 denote the velocity of this ball before the contact, and let
denote the velocity of this ball before the contact, and let
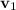 denote the velocity of the ball after the contact.
denote the velocity of the ball after the contact.
Momentum
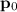 of this ball before the contact:
of this ball before the contact:
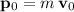 .
.
Momentum
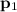 of this ball after the contact:
of this ball after the contact:
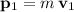 .
.
Impulse, which is equal to the change in momentum:
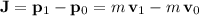 .
.
Since the velocity of the ball after the contact is in the
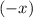 direction,
direction,
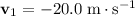 . The average external force on this ball would be:
. The average external force on this ball would be:
 .
.
(Rounded to two significant figures.)