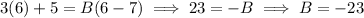Assume
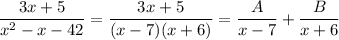
Combining the fractions on the right hand side gives
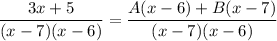
The fractions will be equal as long as the their numerator are equal:
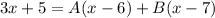
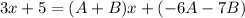
Polynomials are equal to one another if the coefficients of like terms are equal:
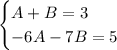
Solving this, you'd get
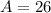 and
and
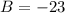 , so that your answer would be (26, -23).
, so that your answer would be (26, -23).
- - -
Instead of solving the system of equations above, there is a trick that involves picking
 so that some terms disappear and solving for either
so that some terms disappear and solving for either
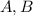 is much faster.
is much faster.
At the point where we have
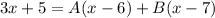
notice that setting
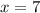 will eliminate
will eliminate
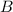 . Doing so, we get
. Doing so, we get

while setting
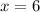 would give
would give