Answer:
The domain of
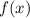 is
is
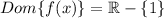 .
.
Explanation:
Let
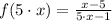 , which is rearranged by algebraic means:
, which is rearranged by algebraic means:
1)
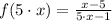 Given
Given
2)
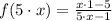 Modulative property
Modulative property
3)
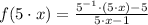 Existence of multiplicative inverse/Associative and commutative properties.
Existence of multiplicative inverse/Associative and commutative properties.
4)
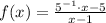 Composition of functions.
Composition of functions.
5)
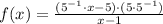 Existence of multiplicative inverse/Associative property.
Existence of multiplicative inverse/Associative property.
6)
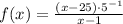 Commutative, associative and distributive properties/
Commutative, associative and distributive properties/
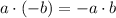 /Definition of subtraction
/Definition of subtraction
7)
![f(x) = (x-25)\cdot [5^(-1)\cdot (x-1)^(-1)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/1wyfyxzzz1uci10udmjtzjsx8chuxadm72.png) Definition of division/Associative property
Definition of division/Associative property
8)
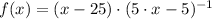
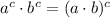 /Distributive property/
/Distributive property/
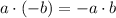 /Definition of subtraction
/Definition of subtraction
9)
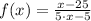 Definition of division/Result
Definition of division/Result
The domain of a polynomial-based rational function consists in all values of the real set except values where denominator equals zero. The value of
 such that rational function becomes undefined is:
such that rational function becomes undefined is:
1)
 Given
Given
2)
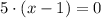 Distributive property
Distributive property
3)
![[5\cdot (x-1)]\cdot 5^(-1) = 0\cdot 5^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/9mxmwj7z7sup878tkelpsac0i117rmk0wv.png) Compatibility with multiplication
Compatibility with multiplication
4)
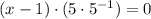 Commutative and associative properties/
Commutative and associative properties/
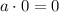
5)
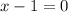 Existence of multiplicative inverse/Modulative property
Existence of multiplicative inverse/Modulative property
6)
![x+[1+(-1)] = 1+0](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/om6zzcxxs4v1vsvkdfk8tl4o2bikmc69ud.png) Compatibility with addition/Commutative and associative properties
Compatibility with addition/Commutative and associative properties
7)
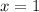 Existence of additive inverse/Modulative property/Result
Existence of additive inverse/Modulative property/Result
Hence, the domain of
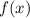 is
is
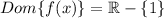 .
.