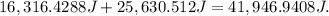Final answer:
The total mechanical energy of the ski jumper is 41,946.9408 J, which is the sum of the kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy.
Step-by-step explanation:
To determine the total mechanical energy of the ski jumper, we need to consider two types of energy: kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy.
The kinetic energy is given by the equation KE = 0.5 * mass * speed^2. Plugging in the values, we get KE =
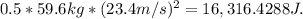
The gravitational potential energy is given by the equation PE = mass * gravity * height. Plugging in the values, we get
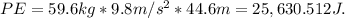
To find the total mechanical energy, we simply add the kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy: E = KE + PE =