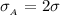Answer:
The surface charge density on planes A and B respectively is
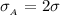
and
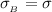
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The electric field in region to the left of A is
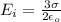
The direction of the electric field is left
The electric field in the region to the right of B is
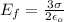
The direction of the electric field is right
The electric field in the region between the two planes is
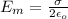
The direction of the electric field is right
Let the surface charge density on planes A and B be represented as

From the question we see that
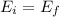
Generally the electric to the right and to the left is due to the combined electric field generated by plane A and B so
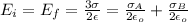
=>
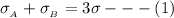
Generally the electric field at the middle of the plane A and B is due to the diffencence in electric field generated by plane A and B
i.e
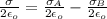
=>
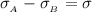
=>
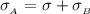
From equation 1
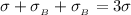
=>
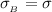
So
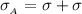
=>