Answer:
n R ln(Vf/Vi)
Step-by-step explanation:
Entropy is the loss of energy available to do work. Entropy is a state function (i.e. it depends only upon the current state of the system and is independent of how that state was prepared).
Since the temperature change of the ideal is constant, hence this is an isothermal expansion of a perfect gas. The change in entropy (ΔS) for an isothermal expansion of a perfect gas is given by:
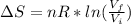
Where n is the amount of gas molecules in mol and R is the gas constant in JK⁻¹mol⁻¹given by R =
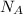 k, k is Boltzmann's constant in J K⁻¹ and Avogadro's constant
k, k is Boltzmann's constant in J K⁻¹ and Avogadro's constant
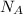 in mol⁻¹. Vf is the final volume and Vi the initial volume.
in mol⁻¹. Vf is the final volume and Vi the initial volume.