Answer:
0.0457 M
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction that takes place is:
- 2HBr + Ca(OH)₂ → CaBr₂ + 2H₂O
First we calculate how many moles of acid reacted, using the HBr solution's concentration and volume:
- Molarity = Moles / Volume
- Molarity * Volume = Moles
- 0.112 M * 12.4 mL = 1.389 mmol HBr
Now we convert HBr moles to Ca(OH)₂ moles, using the stoichiometric ratio:
- 1.389 mmol HBr *
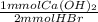 = 0.6944 mmol Ca(OH)₂
= 0.6944 mmol Ca(OH)₂
Finally we calculate the molarity of the Ca(OH)₂ solution, using the given volume and calculated moles:
- 0.6944 mmol Ca(OH)₂ / 15.2 mL = 0.0457 M