Prove:
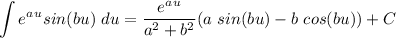
Integration by parts formula:
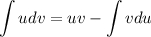
Find u, du, v, and dv for this function:
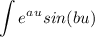
Plug these values into the IBP formula.
Multiply and simplify the factors. Factor the negative out of the integral.
Factor out a/b from the integral.
Now we are going to apply IBP to the function:
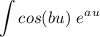 . Find u, du, v, and dv for this function.
. Find u, du, v, and dv for this function.
Plug these values into the IBP formula.
Multiply and simplify the factors.
Factor out a/b from the integral.
Notice that we have the same integral we started with. Let's plug this integral into the original IBP we did.
Distribute a/b inside the parentheses.
Factor 1/b out of the right side of the equation.
Multiply both sides by b to get rid of 1/b.
Add the integral to both sides of the equation.
Factor the integral on the left side.
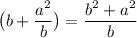 , so we can multiply both sides of the equation by
, so we can multiply both sides of the equation by
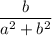 .
.
Simplify the equation before multiplying everything by
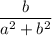 .
.
Multiply the two factors together. Notice that the two b's in the denominator and numerator, respectively, cancel out. We are left with:
Factor
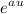 from the numerator.
from the numerator.
Split the numerator and denominator to make it appear the same as the original question.
Since we are taking the integral of something, we can add a +C at the end to complete the problem.
This is equivalent to the proof that we are given, therefore, we proved the integral correctly.