Answer:
v₃ = 2 [m/s]
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve such problems we must use the principle of conservation of momentum. That is, the linear momentum is conserved before and after the collision.
P = m*v
where:
P = linear momentum [kg*m/s]
m = mass [kg]
v = velocity [m/s]
The momentum is conserved before and after the collision, in this way we can obtain the following equation.
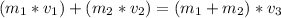
where:
m₁ = mass of the cart moving = 4 [kg]
v₁ = velocity of the cart moving before the collision = 3 [m/s]
m₂ = mass of the cart initially at rest = 2 [kg]
v₂ = velocity of the cart at rest = 0
v₃ = velocity of the two carts combined (carts stick together) after the collision [m/s]
![(4*3)+(2*0)=(4+2)*v_(3)\\v_(3)=12/6\\v_(3)=2[m/s]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/npv9c3uz0j7if1g0x1n472fwuof0jtfnrl.png)