Answer:
5.30
Step-by-step explanation:
The pH of a buffer given by the Henderson-Hasselbach equation can be expressed as:
![pH = pKa + log ([salt])/([Acid])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/4zl0ojkli6dx7ep40clcj7ia8dxo6cdr6v.png)
Given that:
Volume of the solution = 100.0 mL
To liters; the volume of the solution be 0.1 L
The concentration of
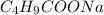 = 0.20 M
= 0.20 M
The concentration of
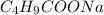 = molarity × volume
= molarity × volume
The concentration of
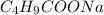 = 0.20 mol/L × 0.1 L
= 0.20 mol/L × 0.1 L
The concentration of
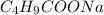 = 0.02 mol
= 0.02 mol
The concentration of
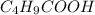 = 0.20 M
= 0.20 M
The concentration of
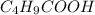 = 0.20 mol/L × 0.1 L
= 0.20 mol/L × 0.1 L
The concentration of
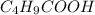 = 0.02 mol
= 0.02 mol
However, the number of moles of NaOH added = 0.01 moles
Now; The ICE table can be computed as:
C₄H₉COOH + OH⁻ ⇄ C₄H₉COO⁻ + H₂O
Initial 0.02 0.01 0.02
Change - 0.01 -0.01 +0.01 +0.01
Equilibrium 0.01 - 0.03 0.01
Recall that the pH of
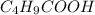 = 4.82
= 4.82
∴
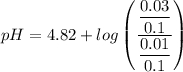
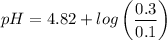
pH = 4.82 + log ( 3 )
pH = 4.82 + 0.4771
pH = 5.2971
pH ≅ 5.30