Answer:
-1
Explanation:
the "slope" of a graph is rise / run
you divide the "rise" from one point on a graph to another by the "run" from one point to another.
We can use any two points on a graph to find this value. (There are other ways to find slope, but this is the easiest method for find the slope of a graphed line)
We can see two points on the line already pointed out, but we can also look to see other points (that require less math)
[remember, points are written as (x,y) ]
We can see a point at (1,0) and another point at (0, 1)
the "rise" between two points is the difference in y-values.
0 - 1 = -1
{you can also look at the graph/count the boxes}
So, the rise between these two points is -1.
(really, it's a drop)
the "run" between these two points is the difference in x-values.
1 - 0 = 1
so, the run between these two points is 1.
Now, all that's left to do is divide the rise / run:
-1 / 1 = -1
So, the slope of this line is -1.
this can be summed up in the following formula:
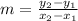
where
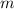 is the slope of the graph,
is the slope of the graph,
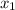 = x-value of first point on graph
= x-value of first point on graph
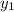 = y-value of first point on graph
= y-value of first point on graph
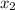 = x-value of second point on graph
= x-value of second point on graph
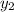 = y-value of second point on graph
= y-value of second point on graph
the equation of a line
y = mx + b
incorporates the slope (as
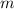 )
)