Answer:
Scale factor is
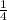 .
.
Explanation:
Given the coordinates of
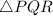 as:
as:
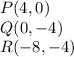
And the coordinates of
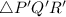 as:
as:
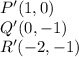
To find:
The scaling factor of the dilation to transform the
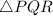 to
to
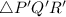 .
.
Solution:
First of all, let us find the distance between the vertices i.e. the sides of the triangle.
Distance formula:
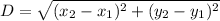
Where
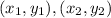 are the coordinates of two points between which the distance is to be calculated.
are the coordinates of two points between which the distance is to be calculated.
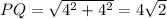
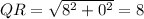
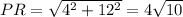
Now, let us find the sides of the
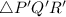 :
:
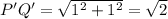
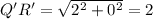
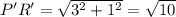
We can clearly see that, the sides of
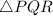 are four times the corresponding sides of
are four times the corresponding sides of
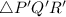 .
.
Therefore, the scaling factor is
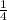 .
.
Please refer to the attache image in the answer area.