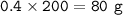Mass of CaBr₂ : 80 g
Further explanation
Reaction
Ca+2Br⇒CaBr₂
mass of Ca = 20 g
mol of Ca (MW=40 g/mol):
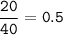
mass of Br = 64 g
mol Br(80 g/mol) :
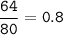
Ca remains at the end of the reaction⇒ Ca as an excess reactant
20% Ca remains(unreacted) :
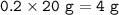
Ca reacted :
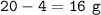
mol Ca reacted :
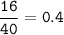
mol CaBr₂ = mol Ca reacted = 0.4
mass CaBr₂ (MW=200 g/mol) produced :
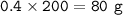
Or you can use mol ratio from equation :
mol CaBr₂ : mol Br (as limiting reactant) = 1 : 2, so mol CaBr₂ :
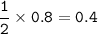
mass CaBr₂ (MW=200 g/mol) produced :