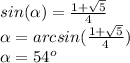Answer:
Alpha is 54 degrees
Explanation:
We can use the addition identities for cosine and for sine to express the given equation in terms of sine and cosine of alpha:
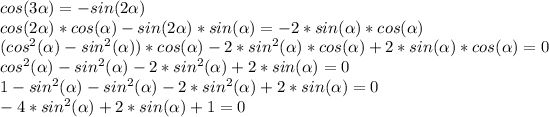
we can use the quadratic formula to find what sine of alpha is:
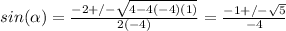
and for
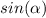 to be positive (acute angle in the first quadrant) the answer is:
to be positive (acute angle in the first quadrant) the answer is: