Answer:
C₂ = 2.22 KJ/kg °C
Step-by-step explanation:
Since, both objects are in thermal contact. Therefore, the law of conservation of energy tells us that:
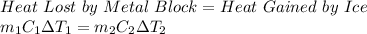
where,
m₁ = mass of ice = 1 kg
C₁ = specific heat of ice = 2.04 KJ/kg.°C
ΔT₁ = Change in Temperature of Ice = -8.88°C - (-24°C) = 15.12°C
m₂ = mass of metal block = 1 kg
C₂ = specific heat of metal = ?
ΔT₂ = Change in Temperature of Metal Block = 5°C - (-8.88°C) = 13.88°C
Therefore, using these values in the equation, we get:
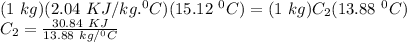
C₂ = 2.22 KJ/kg °C