Answer:
- modulus: 3√2
- argument: -3π/4 (or 5π/4)
Explanation:
The modulus is the magnitude of the complex number; the argument is its angle (usually in radians).
__
rectangular form
The complex number can be cleared from the denominator by multiplying numerator and denominator by its conjugate:
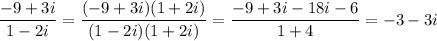
polar form
The magnitude of this number is the root of the sum of the squares of the real and imaginary parts:
modulus = √((-3)² +(-3)²) = 3√2
The argument is the arctangent of the ratio of the imaginary part to the real part, taking quadrant into consideration.
arg = arctan(-3/-3) = -3π/4 or 5π/4 . . . . radians
__
modulus∠argument = (3√2)∠(-3π/4)