Answer:
The fish is experiencing a water pressure of 502.8 kPa.
Step-by-step explanation:
The water pressure the fish is experiencing can be found as follows:
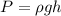 (1)
(1)
Where:
g: is the gravity = 9.81 m/s²
h: is the height (depth) = 50.0 m
ρ: is the seawater's density = 1.025 g/cm³
By replacing the above values into equation (1) we have:
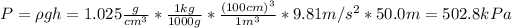
Therefore, the fish is experiencing a water pressure of 502.8 kPa.
I hope it helps you!