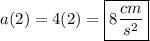Hello!
Begin by plugging in the values for m and n. We get the equation for the velocity of the particle to be:
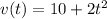
A.
To find the change in velocity over the interval (2s ≤ t ≤ 5s), we can simply find the difference in the velocities at these times.
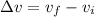
For this situation:
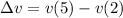
Substitute these times for 't' into the equation and solve.
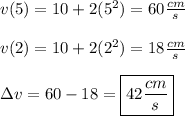
B.
To find the average acceleration, we must take the SLOPE of the velocity function over this interval using the slope formula:
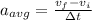
Plug in the values for the particle's velocity at t = 2 s and 5 s that we solved for above.
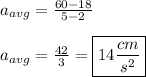
C.
The instantaneous acceleration can be found by taking the derivative of the v(t) function using the power rule. Recall:
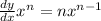
Using this rule:
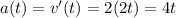
Substituting in t = 2 s: