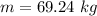Answer:
The value is
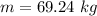
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The value of the external force is
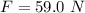
The magnitude of the astronaut's acceleration is
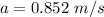
Generally Newton's Second Law of Motion from the mass of the astronauts is mathematically represented as
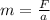
=>
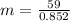
=>