Plotting the graph between current (I) and potential difference (V) allows the determination of the resistance (R) of the resistor by analyzing the slope of the resulting straight line.
To determine the resistance (R) of the given resistor, we can plot a graph between current (I) and potential difference (V) using the provided data. According to Ohm's Law, the relationship between current, potential difference, and resistance is given by the equation V = IR.
Using the given data points (V, I), plot the current (I) on the y-axis and potential difference (V) on the x-axis. A linear relationship in the form of a straight line passing through the origin indicates a resistor with constant resistance.
After plotting the graph, the slope of the line represents the resistance (R) according to Ohm's Law
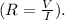 The reciprocal of the slope gives the resistance.
The reciprocal of the slope gives the resistance.
For a straight-line graph, the equation can be written as y = mx, where (y) is the dependent variable (I), m is the slope, and x is the independent variable (V).
In this case, the slope m is equal to R, the resistance of the resistor.
In summary, by plotting a graph between current (I) and potential difference (V), the resistance (R) of the resistor can be determined by finding the slope of the line, indicating the constant relationship between current and potential difference according to Ohm's Law.